Ectoin®
INCI: ECTOIN
Origin of Ectoin®
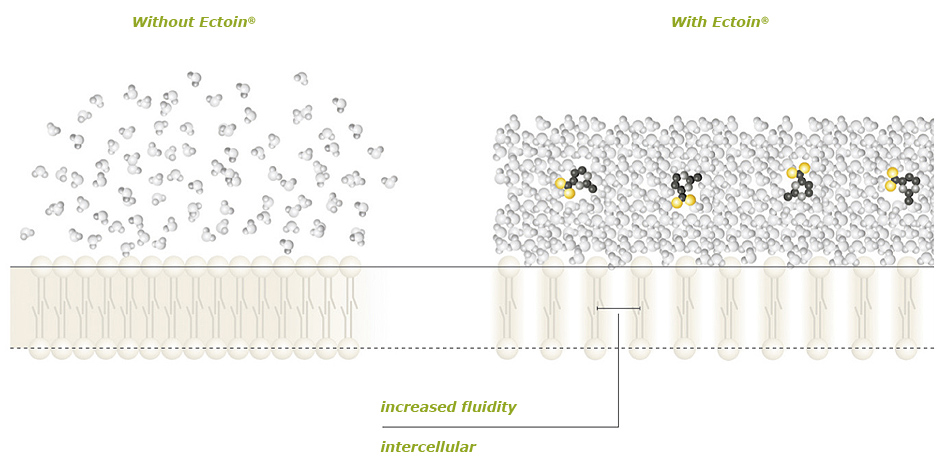
From a chemical point of view, and as an amino acid derivate, Ectoin® is a small molecule and has cosmotropic properties. Cosmotropes contribute to the stability and structure of water-water interactions.
They cause water molecules to interact favorably, which also stabilizes intermolecular interactions in biomolecules such as proteins.
Transferred to a biological system, this means that Ectoin® surrounds itself and its neighboring proteins or cell membranes with a water layer. This structure is named the “Ectoin® Hydro Complex.””
Picture credit: ectoin.com
Salt lakes and deserts are the most hostile environments on Earth. Despite this, highly adapted so-called extremophilic microorganisms fight dryness and extreme changes in temperature and manage to prosper. The reason for this is a substance called Ectoin®, which protects these organisms from harmful environments.
Ectoin® was discovered in 1985 and since then has been investigated in detail.
Today, the outstanding cell-protection properties of Ectoin® find applications in medical devices and products for the life science industry.
Picture credit: ectoin.com
.
Ectoin® is used for the symptomatic treatment of inflammatory skin diseases, such as e.g. eczema (atopic dermatitis), psoriasis, contact dermatitis or radio dermatitis.
Ectoin® supports the regeneration process of the skin, protects against new damage, reduces erythema and smoothens the skin.
Ectoin® also reduces the itchiness that is associated with inflammatory skin diseases.
Ectoin® is a natural substance proven to prevent UVA-induced premature photoaging. Ectoin works by inhibiting UVA-induced second messenger release.
A study (1) published by Skin Pharmacology and Physiology in 2004 indicates that Ectoin protects the skin from UVA-induced cellular damage in many ways. The study confirms that the UVA-induced second messenger release, transcription factor AP-2 activation, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression, and mitochondrial DNA mutation could be prevented through the administration of ectoin.
The results demonstrate that Ectoin prevents the effects of UVA-induced and accelerated skin ageing at different cell levels.
Reference:
Elucidation of the anti‐aging effects of ectoine using cdna microarray analysis and signaling pathway evaluation; S. Anzali A. Von Heydebreck T. Herget; First published: 02 July 2010
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2494.2010.00589_4.x
Further scientifically relevant research regarding Ectoin®:
DNA protection: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29127339
Protectant: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28033102
Stress protectant: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29565833